What is Telematics? 📡
Telematics refers to the combination of telecommunication and informatics, enabling the transmission of data from vehicles to remote systems in real-time. It’s widely used in connected vehicles, fleet management, and IoT systems for monitoring vehicle performance, tracking location, and enhancing driver safety.
In simple terms, telematics is the technology that powers connected cars and vehicle tracking systems.
Key Components of Telematics
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Tracks vehicle location and movement.
- Onboard Diagnostics (OBD): Monitors vehicle health and performance (engine status, fuel level, etc.).
- Wireless Communication (4G/5G): Transfers real-time data to cloud servers or fleet management systems.
- Data Processing Unit: Analyzes and processes data for actionable insights.
- Cloud/Backend Systems: Stores and analyzes the data for reporting and visualization.
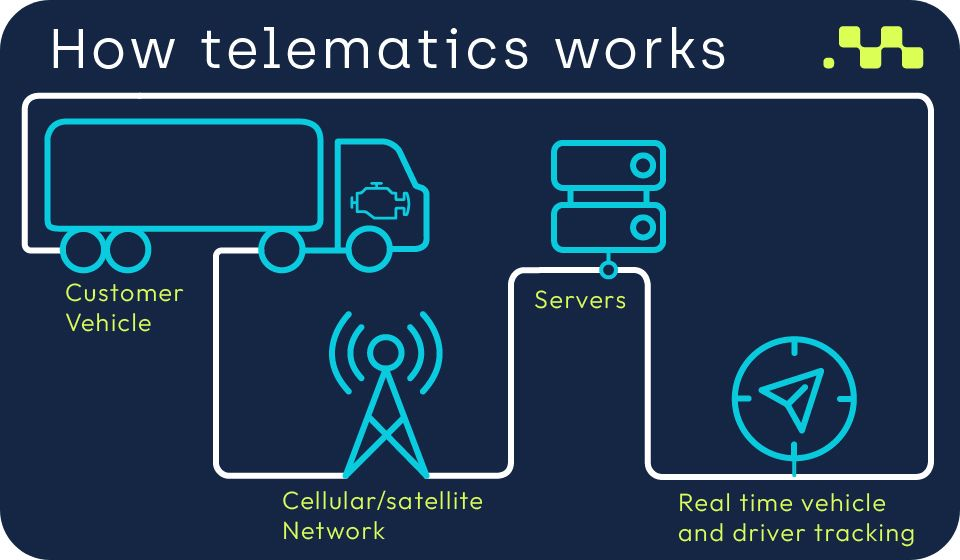
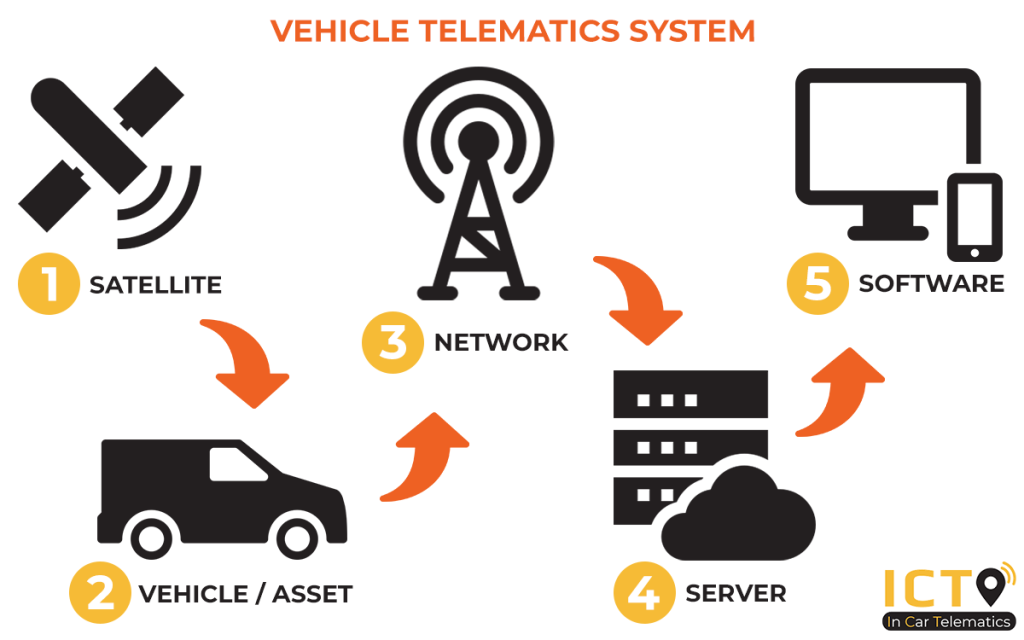
How Telematics Works
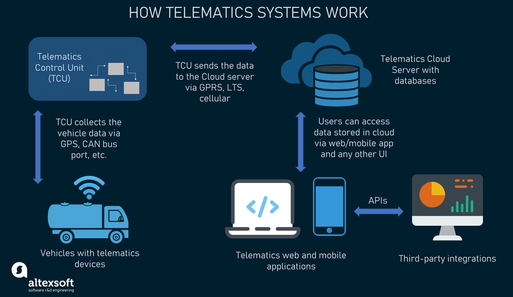
- Data Collection: Sensors in the vehicle collect data (location, speed, fuel level, engine status, etc.).
- Data Transmission: The data is transmitted via cellular networks to a cloud server.
- Processing and Analysis: The server processes the data to generate insights (e.g., trip history, alerts).
- User Interface: Fleet managers, drivers, or users access data through a web or mobile dashboard.
Applications of Telematics
- Fleet Management:
- Vehicle tracking and route optimization.
- Monitoring driver behavior and fuel consumption.
- Preventive maintenance based on real-time diagnostics.
- Connected Cars:
- Real-time traffic updates and navigation.
- Remote diagnostics and over-the-air (OTA) updates.
- Emergency response in case of accidents (eCall systems).
- Insurance Telematics:
- Usage-based insurance (pay-as-you-drive).
- Risk assessment based on driving behavior.
- Logistics and Delivery:
- Real-time package tracking and delivery status updates.
- Reducing idle time and improving delivery accuracy.
Benefits of Telematics
- Improved Efficiency: Optimizes routes, reduces fuel consumption, and prevents vehicle downtime.
- Enhanced Safety: Monitors driver behavior and provides alerts for harsh driving, speeding, or potential hazards.
- Cost Savings: Reduces operational costs through efficient resource management.
- Predictive Maintenance: Prevents unexpected breakdowns by analyzing vehicle health in real-time.
Examples of Telematics Devices and Services
- Vehicle Tracking Systems (GPS) – For fleet management and logistics.
- OBD-II Devices – Monitors vehicle health and diagnostics.
- Dash Cameras with Telematics – Records driving behavior and provides real-time alerts.
- Connected Car Systems – Services like Tesla’s Autopilot or GM’s OnStar.
Conclusion
Telematics is transforming industries like automotive, logistics, and insurance, providing real-time insights that improve efficiency, safety, and performance. It’s the backbone of connected cars, fleet management, and IoT-based monitoring solutions.